Coronary artery disease
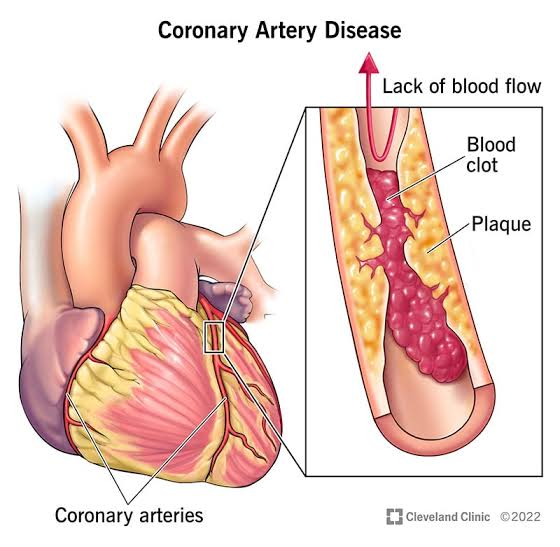
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE (CAD) The commonest form of coronary artery disease is narrowing of the vessel lumen by atherosclerotic plaque(s).The most frequent symptom of CAD is chest pain (angina pectoris) due to myocardial ischemia. Coronary Arteries There are two main coronary arteries which branch to supply the entire heart. They are named the left and right coronary arteries,and arise from the left and right aortic sinuses within the aorta. Branches of Left coronary artery are: 1. Left anterior descending artery (LAD) or anterior interventricular artery 2. Left marginal artery (LMA) 3. Left circumflex artery (Cx) Branches of Right coronary artery are: 1. Right Marginal artery 2. Posterior interventricular artery MYOCARDIAL ISCHEMIA Ischemia results in immediate changes which can be detected by echo: Abnormalities of wall motion (hypokinetic, akinetic, dyskinetic) Abnormalities of wall Thickening Abnormalities of overall LV function (e.g. EF) These can be detected by 2-D ec...


